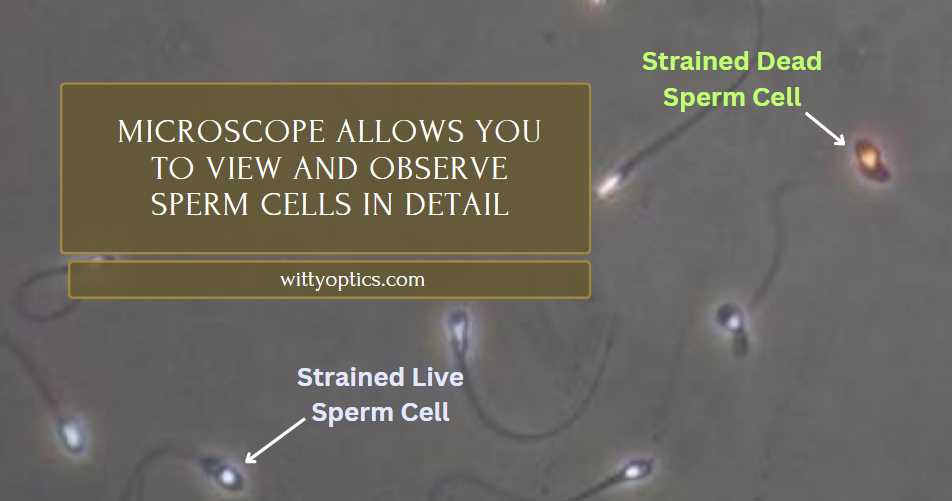
Yes, you can see your sperm with a microscope. Microscopy allows you to view and observe sperm cells in detail, providing valuable insights into their structure and function.
Sperm cells are typically around 5 micrometers in size, which is small but still visible under a microscope. A standard compound light microscope, commonly found in laboratories and schools, should suffice for observing sperm cells. However, to see them clearly, you may need to use a higher magnification objective lens, such as a 40x or 100x lens.
Additionally, staining techniques can be employed to enhance the visibility of sperm cells under the microscope. Overall, with the right equipment and preparation, it’s entirely possible to view your sperm under a microscope.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Average sperm size | 5 micrometers |
| Magnification needed | 40x – 100x |
| Staining techniques | Enhance visibility |
| Common microscope type | Compound light microscope |
| Accessibility | Laboratories, schools, research facilities |
| Additional equipment required | Staining kits, high magnification lenses |
Sperm are also very small, so yes, you can see them with a microscope!
Here’s how it works:
- Get a Microscope: First, you’ll need a microscope. It’s a special tool with lenses that magnify tiny objects.
- Prepare a Sample: You’ll need a sample of sperm to look at. This usually means collecting semen, which contains sperm. You can collect it by masturbating or using a special condom during sex.
- Prepare the Slide: To look at the sperm under the microscope, you’ll put a tiny drop of the semen on a glass slide. Then, cover it with a thin piece of glass called a cover slip.
- Look Through the Microscope: Place the slide on the microscope’s stage and look through the eyepiece. Start with a low magnification and gradually increase it until you see the sperm clearly.
- Observe and Study: Once you’ve found the sperm, you can observe their shape, movement, and other characteristics. Sperm are tiny, tadpole-like cells with a head and a tail that helps them swim.
Remember to handle the microscope and slides carefully and follow any safety guidelines that come with the microscope. And always remember, it’s perfectly normal to be curious about your body and how it works!
Understanding Sperm
As I looked through the microscope’s eyepiece, I started with a low magnification and gradually increased it until I saw the sperm clearly. It was incredible to see these tiny, tadpole-like cells swimming around. I observed their shape, movement, and even noticed differences between individual sperm.
Handling the microscope and slides carefully was crucial, and I made sure to follow all safety guidelines. Exploring sperm under the microscope was not only educational but also a reminder of the wonders of the human body.
Sperm are male reproductive cells produced in the testicles. They are essential for fertilizing female eggs and initiating pregnancy. Structurally, sperm consist of a head, midpiece, and tail, designed for mobility towards the egg. Studying sperm is crucial for understanding fertility and reproductive health.
Exploring sperm under the microscope not only satisfied my curiosity about the male reproductive system but also deepened my understanding of the miracle of conception. It was a hands-on experience that left me with a sense of wonder and respect for the incredible journey that each sperm undertakes in the quest for fertilization.
Microscopes
Microscopes are instruments that magnify small objects, allowing for detailed observation. They come in various types, including optical, electron, and digital microscopes. Optical microscopes, commonly used for educational and basic research purposes, employ visible light to magnify specimens.
| Principle of Operation | Applications | |
| Optical Microscope | Uses visible light | Education, research |
| Electron Microscope | Uses electron beams | High-resolution imaging |
| Digital Microscope | Integrates with computers | Digital imaging, analysis |
Can You See Sperm with a Microscope?
While microscopes can magnify objects significantly, the size of sperm presents challenges for direct observation. Sperm are typically around 50 micrometers long, requiring high-magnification microscopes for clear visualization. Optical microscopes, though useful for larger specimens, may not provide adequate magnification for viewing sperm.
| Type of Microscope | Magnification Range | Suitability for Sperm Observation |
| Optical Microscope | Up to 1000x | Limited due to sperm size |
| Electron Microscope | Up to 1,000,000x | Suitable for detailed sperm analysis |
| Digital Microscope | Varies | Depends on magnification capability |
Steps to View Sperm with Microscope
If you’re interested in viewing your sperm using a microscope, there are specific steps you can follow to achieve this:
- Preparation of Microscope: Begin by setting up your microscope on a stable surface and ensuring it is clean and properly aligned. Adjust the lighting and focus mechanisms to optimize visibility.
- Preparation of Sperm Sample: Collect a semen sample using a clean and sterile container. Place a small drop of the sample onto a glass slide and cover it with a coverslip to prevent evaporation and contamination.
Viewing Sperm Under Microscope: Place the prepared slide onto the microscope stage and adjust the magnification to the highest level possible. Use the focus knobs to bring the sperm cells into clear view, adjusting the lighting as needed for optimal contrast
Alternative Methods to View Sperm
If you’re unable to visualize sperm using a microscope at home, there are alternative methods available:
Sperm Analysis Centers
Consider visiting a specialized fertility clinic or laboratory that offers sperm analysis services. These facilities have advanced equipment and trained professionals who can provide detailed assessments of sperm health and fertility.
DIY Methods
Explore DIY sperm analysis kits available on the market, which typically include instructions and materials for collecting and observing sperm samples at home. While these kits may not offer the same level of accuracy as professional analysis, they can provide valuable insights into sperm health and concentration.
Safety Precautions and Best Practices
When using a microscope to view sperm or any other biological specimen, it’s essential to observe safety precautions to prevent contamination and ensure accurate results. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Cleanliness and Sterility: Maintain a clean work environment and sterilize all equipment before and after use to avoid contamination of samples.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety goggles or glasses to protect your eyes from potential splashes or spills when handling biological samples.
- Proper Handling of Microscope: Handle the microscope with care to avoid damage and ensure accurate results. Follow manufacturer instructions for maintenance and cleaning.
What type of microscope do I need to see my sperm?
To visualize your sperm effectively, you’ll need a high-powered microscope with a magnification of at least 400 times. Light microscopes, commonly found in schools and laboratories, may not offer sufficient magnification for clear visualization of sperm cells. Preferably, an electron microscope would be ideal for observing sperm at a cellular level due to its high magnification capabilities.
|
Type of Microscope |
Features |
|
Light Microscope |
Limited magnification; suitable for educational purposes. |
|
Electron Microscope |
High magnification; provides detailed images at the cellular level. |
|
Fluorescence Microscope |
Excels in visualizing fluorescently labeled specimens. |
What magnification is required to see sperm with a microscope?
To see sperm cells with a microscope, you’ll need a magnification level of at least 400x to 1000x. This level of magnification is essential for resolving the small size of sperm cells, which typically range from 3 to 5 micrometers in length. Low magnification microscopes may not provide sufficient resolution to visualize sperm cells clearly, so it’s recommended to use a microscope with high magnification capabilities, such as an electron microscope, for optimal results.
Can I prepare my own sperm sample for viewing under a microscope?
Yes, you can prepare your own sperm sample for viewing under a microscope. Start by collecting a semen sample in a clean, sterile container. Then, place a small drop of the semen onto a glass slide and cover it with a coverslip to prevent evaporation and contamination. Finally, place the prepared slide onto the microscope stage and adjust the focus to bring the sperm cells into clear view.
How do I prepare a sperm sample for microscope observation?
To prepare a sperm sample for microscope observation, follow these steps:
-
Collect Semen: Obtain a sample of semen containing sperm. This can be done through masturbation or using a special condom during sexual activity.
-
Prepare a Clean Slide: Clean a glass microscope slide and cover slip with alcohol or a mild detergent to remove any contaminants. Ensure they are completely dry before use.
-
Apply Sample: Place a small drop of semen onto the center of the microscope slide. Be careful not to use too much, as excess fluid can cause the cover slip to float and distort the sample.
-
Add Cover Slip: Gently lower a clean cover slip onto the drop of semen, taking care to avoid trapping air bubbles. The cover slip helps flatten the sample and protects it from drying out.
-
Observe Under Microscope: Place the prepared slide on the microscope stage and secure it in place. Begin with a low magnification objective lens and gradually increase the magnification until sperm are visible.
-
Focus and Adjust: Use the microscope’s focus and adjustment knobs to sharpen the image of the sperm. You may need to adjust the lighting and contrast settings for better clarity.
-
Observe and Record: Once sperm are in focus, observe their movement, shape, and other characteristics. You can also capture images or videos of the sperm for further analysis or documentation.
-
Clean Up: After observation, carefully discard the slide and cover slip or clean and sterilize them for future use. Clean the microscope stage and lenses to remove any residue.
By following these steps, you can prepare a sperm sample for microscope observation and gain valuable insights into sperm morphology and motility.
Can I use a DIY sperm analysis kit to view my sperm at home?
Yes, you can use a DIY sperm analysis kit to view your sperm at home. These kits typically provide materials and instructions for collecting and observing sperm samples independently. While DIY kits may not offer the same level of accuracy as professional analysis, they can provide valuable insights into sperm health and concentration, making them a convenient option for at-home testing.
|
DIY Sperm Analysis Kit |
Features |
|
Convenience |
Provides materials and instructions for collecting and observing sperm samples at home. |
|
Accuracy |
May not offer the same level of accuracy as professional analysis. |
|
Insights |
Provides valuable insights into sperm health and concentration. |
Are there any safety precautions I should follow when viewing sperm with a microscope?
Yes, there are several safety precautions you should follow when viewing sperm with a microscope.
|
Safety Precautions |
Guidelines |
|
Eye Protection |
Wear safety goggles or glasses to protect eyes from potential splashes or spills. |
|
Cleanliness |
Maintain a clean work environment and sterilize equipment to avoid contamination. |
|
Handling Microscope |
Handle the microscope with care to prevent damage and ensure accurate results. |
Final words
While it is technically possible to see sperm with a microscope, the type of microscope and its magnification power are crucial factors in achieving clear and detailed images. Light microscopes, commonly used for educational and hobbyist purposes, may not provide sufficient magnification for visualizing sperm cells effectively. However, higher magnification microscopes, such as electron microscopes, can offer detailed insights into sperm structure and morphology. If you’re interested in exploring your sperm under a microscope, ensure you follow proper safety precautions and consider alternative methods if necessary. Remember, the ability to see sperm with a microscope can vary depending on the equipment available and the quality of the sample.

I am an enthusiastic student of optics, so I may be biased when I say that optics is one of the most critical fields. It doesn’t matter what type of optics you are talking about – optics for astronomy, medicine, engineering, or pleasure – all types are essential.