In the vast realm of photography, the lens you choose can make or break your shot. Understanding the nuances of camera lenses is crucial for any photographer aiming to capture that perfect moment. As someone who has navigated the maze of lens choices, let me guide you through the process of choosing the right lens for your camera.
Camera lenses are the eyes of your photographic vision, each with its unique characteristics and capabilities. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of lens selection, covering everything from types of lenses to key features, and providing valuable tips for making an informed decision.
Understanding Camera Lenses: A Comprehensive Overview

Camera lenses are the eyes of a photographer, translating their creative vision into captivating images. Understanding the diverse types of lenses, their compatibility with different camera bodies, and the intricate relationship between aperture and focal length is crucial for any photographer looking to master their craft.
Types of Camera Lenses
- Prime Lenses: Prime lenses have a fixed focal length, meaning they don’t zoom in or out. These lenses are renowned for their exceptional image quality, wide apertures, and suitability for low-light conditions. A 50mm prime lens, for instance, is a popular choice for its versatility and ability to produce stunning background blur.
- Zoom Lenses: Zoom lenses offer variable focal lengths, allowing photographers to zoom in and out on a scene. They provide flexibility in composition, making them a go-to choice for various situations. From the wide-ranging 24-70mm to the powerful 70-200mm, zoom lenses are versatile workhorses.
- Wide-Angle Lenses: Wide-angle lenses have short focal lengths, capturing a broader field of view. Ideal for landscape and architectural photography, these lenses emphasize depth and perspective. A 16mm wide-angle lens, for example, can transform ordinary scenes into dramatic vistas.
- Telephoto Lenses: Telephoto lenses, with long focal lengths, bring distant subjects closer. These lenses are indispensable for wildlife, sports, and portrait photography, providing a magnifying effect without compromising image quality. A 300mm telephoto lens, for instance, can capture distant wildlife with remarkable detail.

Lens Mount Compatibility
Ensuring compatibility between your lens and camera body is paramount. Different camera manufacturers use distinct lens mounts, making it crucial to choose lenses that fit your specific camera model. For instance, Canon and Nikon have proprietary mounts, while mirrorless systems like Sony’s E-mount have gained popularity for their adaptability.
Aperture and Focal Length Explained
- Aperture Settings: Aperture, measured in f-stops, controls the amount of light entering the lens. A lower f-number, such as f/1.4, represents a wider aperture, allowing more light and producing a shallower depth of field. This is advantageous for creative effects like bokeh in portrait photography.
- Focal Length and Its Impact: Focal length dictates the magnification and compression of a scene. A shorter focal length, like 35mm, is considered wide-angle, capturing more of the scene. In contrast, a longer focal length, such as 85mm, is telephoto, bringing distant subjects closer and compressing the background.
To aid in understanding the technical specifications, let’s consider a comparative table showcasing popular lenses:
| Lens Type | Example Model | Aperture Range | Popular Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prime Lens | Canon 50mm f/1.4 | f/1.4-f/16 | Portraits, Low-light |
| Zoom Lens | Nikon 24-70mm f/2.8 | f/2.8 | Versatile, Events |
| Wide-Angle Lens | Sony 16mm f/2.8 | f/2.8-f/22 | Landscapes, Architecture |
| Telephoto Lens | Sigma 300mm f/4 | f/4-f/32 | Wildlife, Sports |
12 Tips to Follow: Choose A Lens

When choosing a lens, it is essential to consider your needs and wants. Given the many available options, it can be challenging to determine what lenses are best for you. We’ve put together some tips on choosing the perfect lens for your shooting style to make things easier.
Purpose of Photography
Before delving into the technical specifications of a lens, it’s essential to define the purpose of your photography. Different genres demand specific characteristics in a lens. Portrait photographers, for instance, often prioritize wide apertures (low f-number) for achieving a beautiful bokeh effect, while landscape photographers may opt for wide-angle lenses to capture expansive scenes.
Budget Considerations
Your budget plays a crucial role in determining the range of lenses available to you. High-end lenses with advanced features often come with a premium price tag. However, there are also excellent mid-range and budget-friendly options that deliver impressive performance. Establishing a budget early in your lens selection process helps narrow down your options and prevents unnecessary financial strain.
Camera Compatibility
Not all lenses are compatible with every camera body. Understanding the lens mount of your camera is crucial to ensure a seamless fit. For example, Canon and Nikon have different proprietary mounts, and the rise of mirrorless cameras introduces additional considerations. Researching your camera’s specifications and compatibility with specific lens mounts ensures a harmonious integration between your camera and lens.
Understanding focal length
When you take a photo, the lens on your camera is focused on an object in front of it. This object becomes the image’s focal point, and everything else is blurry.
Many different focal length lenses are available, affecting photos differently. A short focal length lens will focus on close objects far away, while a long focal length lens will focus on distant objects close up. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
If you’re looking to take photos of people or things that are far away, a long focal length lens is best because it will create less distortion in the image. On the other hand, if you want to take close-up photos of people or things, a short focal length lens is preferable because it won’t distort the image as much.
So which one should you buy? It all depends on what you plan to photograph and what effect you want your photos to have. You can’t just buy any old lens; each has a specific purpose of considering when choosing it.

Point and shoot vs. DSLR camera lenses
Point-and-shoot camera lenses are designed for simple shots that don’t require a lot of control. They usually have a short focal length and a wide-angle lens, which makes them ideal for capturing landscapes, close-ups of people, and other similar scenes.
On the other hand, DSLR camera lenses are geared toward more advanced photography. They typically have a longer focal length and a narrower aperture (which helps to achieve better low-light shooting). They’re also perfect for photos that require more control (like portraits or action shots).
If you’re new to photography, it’s probably best to start with a point-and-shoot camera lens. This will give you enough experience to learn the ropes before moving on to DSLR camera lenses.
Lens Filters
Lens filters are one of the essential components of a camera lens. They help to improve image quality by removing unwanted light and noise from the photo signal. Without them, photos would be blurry and contain a lot of noise.
There are many different lens filters like contact lenses, but Neutral Density (ND) and Circular Polarizer (CP) are the most common. ND filters let less light into the camera lens, while CP filters reduce reflections and reflections from water surfaces. You can also use graduated ND and polarizer filters to boost or minimize intensities in specific directions.
Choosing the right filter for the conditions you’re shooting in is essential. For example, if you’re shooting outdoors in bright sunlight, you’ll need an ND filter to reduce glare and reflections. If you’re taking a portrait, however, an off-the-shoulder dress may reflect too much light into your subject’s face, so using a polarizing filter will help reduce this problem.
Warranty and support
When you buy a camera lens, make sure to read the warranty and support information carefully. Most lenses come with a guarantee that covers defects in materials and workmanship for a period of either one or two years. In addition, most lenses come with some form of support, such as online tutorials or phone support.
If you have any problems with your lens, be sure to contact the manufacturer immediately. They will be able to help you get your lens replaced or fixed as needed. And don’t forget to register your lens with the manufacturer so that you can receive updates and advice on how to use it properly.
Testing Lenses Before Buying
Before you buy a lens, it’s essential to test it out first. This is because lenses can often be incompatible with different cameras, and you don’t want to spend money on something that won’t work.
The best way to do this is by shooting photos or videos with your camera and comparing them to those taken using the lens in question. You can also use online photo comparison platforms like Image Quality Database or LensHunter to see how various lenses perform.

It’s also a good idea to read online reviews of the lens before buying it, as this will give you an idea of how other people have used it and their thoughts about it.
Ideally, it would be best if you aimed to buy a lens that has positive reviews and has been tested on multiple devices to know it will work with your particular camera model.
Image stabilization
Image stabilization is an essential feature because it will help reduce the effects of camera shake, making your photos and videos look blurry.
Some lenses come with built-in image stabilization, while others require you to attach an extra lens or mount to your camera to achieve the same effect. Whichever route you choose, buy a lens with excellent image stabilization capabilities so that your photos and videos will look smooth and precise.
Weight and Size
The weight and size of a lens can impact your overall shooting experience, especially if you plan to be on the move frequently. While a compact prime lens might be lightweight and easy to carry, a large telephoto lens may require additional support and contribute to the overall weight of your camera setup. Consider the balance between portability and the specific needs of your photography style.
Low-Light Performance
For photographers who often find themselves shooting in low-light conditions, such as indoor events or night photography, the lens’s low-light performance becomes crucial. Lenses with wider apertures (e.g., f/1.4 or f/2.8) allow more light to enter, enabling better performance in dimly lit environments.
Autofocus Capabilities
The autofocus capabilities of a lens influence its responsiveness and accuracy in acquiring focus. Fast and reliable autofocus is particularly important in genres like sports or wildlife photography, where capturing fast-moving subjects requires precision. Consider the type of autofocus motor used in a lens (e.g., ultrasonic or linear) and its impact on speed and noise.
To facilitate your decision-making process, let’s create a comparative table outlining key factors for popular lenses:
| Lens Model | Purpose | Budget | Compatibility | Image Stabilization | Weight | Low-Light Performance | Autofocus Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canon 50mm f/1.4 | Portraits | Moderate | Canon EF Mount | No | 290g | Excellent | Ultrasonic |
| Sigma 24-70mm | Versatile | High | Canon/Nikon/Sony EF | Yes | 835g | Good | Hyper Sonic (HSM) |
| Sony 16-35mm | Landscapes | High | Sony E-Mount | Yes | 680g | Good | Linear |
| Nikon 70-200mm | Wildlife/Sports | High | Nikon F Mount | Yes | 1.5kg | Excellent | Silent Wave (SWM) |
Lens Features and Terminology: A Comprehensive Exploration
Understanding the features and terminology associated with camera lenses is essential for photographers seeking to maximize the potential of their gear. From lens coatings to the elusive bokeh effect, each aspect contributes to the overall performance and creative possibilities of a lens.
A. Lens Coatings
Lens coatings play a vital role in enhancing image quality by minimizing unwanted optical phenomena. Coatings, typically applied to lens elements, serve several purposes:
- Anti-Reflective Coating: Reduces lens flare and ghosting caused by reflections off lens surfaces, especially when shooting against bright light sources.
- Water-Repellent Coating: Provides an additional layer of protection against water droplets, making it easier to clean and ensuring unobstructed image capture during adverse weather conditions.
Popular Lens Coatings
| Coating Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Anti-Reflective Coating | Minimizes lens flare and ghosting |
| Water-Repellent Coating | Enhances durability, facilitates cleaning |
| Fluorine Coating | Repels water, oil, and dirt for easy cleaning |
| Nano Coating | Improves light transmission and reduces reflections |
Optical Image Stabilization (OIS)
Optical Image Stabilization is a technology designed to counteract the effects of camera shake, providing sharper images, especially at slower shutter speeds. This feature is particularly valuable in situations where a stable platform, such as a tripod, is not practical.
Lens Image Stabilization Comparison
| Lens Model | Image Stabilization | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Canon 70-200mm f/2.8 | Yes | Handheld stability, improved low-light performance |
| Nikon 24-70mm f/2.8 | Yes | Enhanced sharpness at slower shutter speeds |
| Sony 85mm f/1.4 | Yes | Reduction of motion blur, especially in telephoto ranges |
| Sigma 50mm f/1.4 Art | Yes | Versatility in low-light conditions, handheld shooting |
Focus Motor Types
The focus motor is responsible for driving the autofocus mechanism in a lens. Different types of focus motors offer varying levels of speed, precision, and noise control.
Lens Focus Motor Types
| Lens Model | Focus Motor Type | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Canon 50mm f/1.4 | Ultrasonic (USM) | Fast and quiet autofocus for discreet shooting |
| Nikon 85mm f/1.8 | Silent Wave (SWM) | Smooth and near-silent autofocus for video recording |
| Sony 24-70mm f/2.8 | Linear | Quick and precise autofocus suitable for diverse scenes |
| Sigma 70-200mm f/2.8 | Hyper Sonic (HSM) | High-speed autofocus for capturing fast-moving subjects |
Depth of Field (DoF)
Depth of Field refers to the range of distances within a scene that appears acceptably sharp. It is influenced by factors such as aperture size, focal length, and subject distance.
Aperture and Depth of Field
| Aperture (f-number) | Depth of Field Characteristics |
|---|---|
| f/1.4 – f/2.8 | Shallow depth of field, ideal for portraits |
| f/4 – f/8 | Balanced depth of field, suitable for landscapes |
| f/11 and above | Deep depth of field, advantageous for group shots |
Bokeh Effect
Bokeh refers to the aesthetic quality of the out-of-focus areas in an image. Achieving a pleasing bokeh effect is often a goal in portrait and macro photography.
Bokeh Characteristics of Popular Lenses
| Lens Model | Bokeh Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Canon 85mm f/1.2 | Creamy and smooth bokeh circles |
| Nikon 50mm f/1.8 | Soft and rounded bokeh highlights |
| Sony 135mm f/1.8 | Smooth and well-defined bokeh spheres |
| Fujifilm 56mm f/1.2 | Artistic and appealing bokeh rendition |
Lens Speed
Lens speed refers to the maximum aperture of a lens, impacting its ability to gather light. Faster lenses with wider apertures are advantageous in low-light conditions.
Lens Speed Comparison
| Lens Model | Maximum Aperture (f-number) | Low-Light Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Sigma 35mm f/1.4 Art | f/1.4 | Excellent, ideal for night and indoor shooting |
| Tamron 24-70mm f/2.8 | f/2.8 | Good, suitable for versatile lighting conditions |
| Panasonic 42.5mm f/1.2 | f/1.2 | Outstanding, excels in challenging light situations |
| Zeiss 50mm f/0.95 | f/0.95 | Exceptional, unparalleled low-light capabilities |
Understanding these lens features and terminology empowers photographers to make informed decisions based on their specific needs and creative preferences. By exploring the nuances of coatings, stabilization, focus motors, depth of field, bokeh, and lens speed, you can elevate your photography to new heights, capturing moments with precision and artistic flair.
Comparing Popular Lens Brands and Models: A Comprehensive Analysis

When it comes to camera lenses, the market offers a diverse range of options from various manufacturers. Each brand brings its unique strengths, and understanding the key models they offer is essential for photographers seeking the perfect fit for their camera systems.
Canon
Canon, a stalwart in the imaging industry, has consistently delivered lenses known for their exceptional optical quality and innovation. Popular models include:
Canon Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canon EF 50mm f/1.4 | 50mm | f/1.4-f/16 | Versatile prime for portraits |
| Canon EF 24-70mm f/2.8 | 24-70mm | f/2.8 | Versatility for various shooting scenarios |
| Canon EF 70-200mm f/2.8 | 70-200mm | f/2.8 | Ideal for wildlife, sports, and portraits |
Nikon
Nikon, synonymous with high-quality optics, offers a robust lineup of lenses catering to diverse photographic needs. Key models include:
Nikon Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nikon 50mm f/1.8 | 50mm | f/1.8-f/16 | Prime lens for portraits and low-light |
| Nikon 24-70mm f/2.8 | 24-70mm | f/2.8 | Versatile zoom for a wide range of scenes |
| Nikon 70-200mm f/4 | 70-200mm | f/4-f/32 | Lightweight telephoto for portability |
Sony
Sony has transformed the camera industry with its mirrorless cameras and a growing selection of high-performance lenses. Notable models include:
Sony Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sony FE 85mm f/1.4 | 85mm | f/1.4-f/16 | Ideal for portraits with stunning bokeh |
| Sony FE 24-70mm f/2.8 | 24-70mm | f/2.8 | Professional zoom lens for diverse needs |
| Sony FE 200-600mm f/5.6-6.3 | 200-600mm | f/5.6-6.3 | Super-telephoto for wildlife and sports |
Sigma
Sigma, a third-party manufacturer, has gained acclaim for producing lenses that offer a compelling balance of quality and affordability. Notable models include:
Sigma Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma 35mm f/1.4 Art | 35mm | f/1.4-f/16 | Excellent image quality and bokeh |
| Sigma 24-70mm f/2.8 | 24-70mm | f/2.8 | Versatile zoom with consistent sharpness |
| Sigma 150-600mm f/5-6.3 | 150-600mm | f/5-6.3 | Long telephoto reach for wildlife |
Tamron
Tamron is another third-party manufacturer known for producing lenses that offer a balance of performance and value. Key models include:
Tamron Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tamron 17-50mm f/2.8 | 17-50mm | f/2.8 | Versatile zoom for crop-sensor cameras |
| Tamron 24-70mm f/2.8 | 24-70mm | f/2.8 | Popular choice for all-around shooting |
| Tamron 70-200mm f/2.8 | 70-200mm | f/2.8 | Telephoto zoom with image stabilization |
Fujifilm
Fujifilm, renowned for its mirrorless cameras, has developed a dedicated lineup of lenses for its X-series cameras. Notable models include:
Fujifilm Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fujifilm XF 35mm f/1.4 | 35mm | f/1.4-f/16 | Classic focal length for various genres |
| Fujifilm XF 18-55mm f/2.8-4 | 18-55mm | f/2.8-4 | Versatile zoom with optical image stabilization |
| Fujifilm XF 56mm f/1.2 | 56mm | f/1.2-f/16 | Portrait lens with creamy bokeh |
Pentax
Pentax, though less mainstream, has a loyal following and offers a selection of lenses for its DSLR and mirrorless cameras. Notable models include:
Pentax Lens Comparison
| Lens Model | Focal Length | Aperture Range | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pentax HD DA 35mm f/2.8 Macro Limited | 35mm | f/2.8 | Macro capability with high-resolution optics |
| Pentax HD DA 20-40mm f/2.8-4 Limited | 20-40mm | f/2.8-4 | Compact and weather-resistant zoom lens |
| Pentax HD D FA 70-200mm f/2.8 ED DC AW | 70-200mm | f/2.8 | Professional telephoto zoom with weather sealing |
3 Tips for Buying a Used Lens: A Comprehensive Guide

When considering the purchase of a used lens, a careful evaluation is crucial to ensure you’re getting a quality product that meets your expectations. Follow these tips to make an informed decision:
Inspecting Physical Condition
- Examine the Exterior: Check for scratches, dents, or signs of wear on the lens body. A well-maintained exterior often indicates careful usage.
- Inspect Mount and Contacts: Ensure the lens mount aligns correctly with your camera, and the electrical contacts are clean and undamaged for seamless communication.
Table: Physical Inspection Checklist
| Aspect | Inspection |
|---|---|
| Exterior Condition | Scratches, dents, signs of wear |
| Lens Mount | Alignment with camera body, no damage |
| Electrical Contacts | Clean, undamaged for proper communication |
Checking Optical Quality
- Look for Scratches or Fungus: Examine lens elements for scratches, cracks, or fungus. These issues can significantly impact image quality.
- Test Autofocus and Manual Focus: Ensure smooth and accurate autofocus performance. Check the manual focus ring for any resistance or unusual noises.
Table: Optical Quality Checklist
| Aspect | Inspection |
|---|---|
| Lens Elements | Scratches, cracks, fungus |
| Autofocus Performance | Smooth and accurate |
| Manual Focus | No resistance or unusual noises |
Researching the Lens History
- Check Serial Numbers: Research the lens’s serial number to verify its authenticity and determine its age.
- Ask for Maintenance Records: If available, inquire about any previous repairs or maintenance. A well-documented history is a positive sign.
Table: Lens History Research Checklist
| Aspect | Inspection |
|---|---|
| Serial Number | Verify authenticity and determine age |
| Maintenance Records | Inquire about repairs or maintenance history |
By carefully assessing the physical condition, optical quality, and history of a used lens, you can confidently make a purchase that aligns with your photography needs.

Expert Tips and Tricks: Elevating Your Lens Game
Cleaning and Maintaining Your Lenses
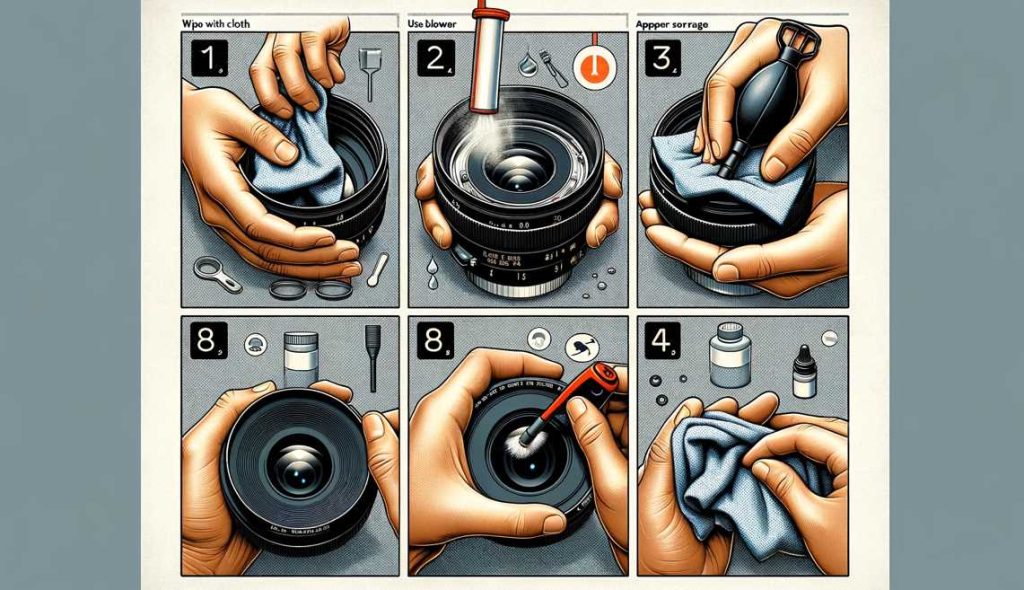
- Use a Gentle Touch: Clean lens elements with a microfiber cloth and a lens-cleaning solution. Apply gentle pressure to avoid scratches.
- Protect with Lens Hoods: Invest in lens hoods to shield your lens from stray light, reduce lens flare, and provide physical protection.
Table: Cleaning and Maintenance Tips
| Tip | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Cleaning Cloth | Microfiber cloth for gentle lens cleaning |
| Lens-Cleaning Solution | Use a specialized solution for effective cleaning |
| Lens Hoods | Invest in hoods for protection against flare and damage |
Lens Accessories and Add-ons
- Filters for Creativity: Experiment with UV, ND, or polarizing filters to add creative effects and protect your lens simultaneously.
- Lens Caps and Rear Caps: Always use lens caps and rear caps when the lens is not in use to safeguard against dust and scratches.
Table: Lens Accessories Tips
| Tip | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Creative Filters | UV, ND, and polarizing filters for effects |
| Lens Caps | Use front and rear caps for comprehensive protection |
Maximizing Lens Performance
- Understand Your Lens: Experiment with different settings and understand the intricacies of your specific lens to unlock its full potential.
- Adapt to Shooting Conditions: Be versatile in adapting to various shooting conditions. Familiarize yourself with your lens’s strengths and limitations.
Table: Maximizing Lens Performance Tips
| Tip | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Experiment and Learn | Understand your lens through trial and error |
| Adaptability | Be versatile in adapting to different scenarios |
By adopting these expert tips, you’ll not only maintain the longevity of your lenses but also unlock their full potential, ensuring each shot is a masterpiece in itself.
Last words
We think now you are pretty much clear about every lens. So, choosing the DSLR lens for your demands will not confuse you anymore. But remember, buying a lens is too much of an affordable thing. So, you should select the best lens which will be perfect for you. And buy the best brand’s lens. We recommend Canon and Nikon lenses, world-class lenses, and DSLR companies. Every professional photographer uses their products.
After reading this article, we hope you all will know all kinds of lenses’ advantages and disadvantages. Thank you so much for reading this article. Have a good day.
Resources and References
- Lens Buying Guides:
- Educational Websites:
- Lens Reviews:
- Online Communities:
- Manufacturer Websites:
- Photography Blogs:
- Video Tutorials:

I am an enthusiastic student of optics, so I may be biased when I say that optics is one of the most critical fields. It doesn’t matter what type of optics you are talking about – optics for astronomy, medicine, engineering, or pleasure – all types are essential.
Last update on 2025-10-08 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
Table of Contents




Pingback: Step-by-Step Guide on How to Care for Camera Lenses (Video Explained)