The difference in binocular magnification affects how steady the image is and what you can see. Higher magnification makes it harder to keep the image still because even small hand movements get amplified. It also gives you a smaller view and can make things look darker. For regular use, binoculars with up to 12x magnification are suggested as they balance zoom with a more stable view and a wider field. The number of binoculars alone doesn’t determine their quality or suitability for a particular purpose.

3 Factors Influencing Binocular Magnification
Optical Configuration and Design
The optical configuration and design of binoculars lay the foundation for effective magnification. In simple terms, it’s how the lenses and prisms inside the binoculars are arranged. The type and quality of glass used, along with the precision in crafting the lenses, significantly impact the clarity and magnification capabilities.
For instance, roof prism binoculars feature a streamlined design, resulting in a more compact and lightweight structure. On the other hand, porro prism binoculars provide a wider field of view due to their offset prism arrangement. Through personal trials with both designs, I’ve noted that the optical configuration influences not only the overall performance but also the ease of use and comfort during extended observations.
Objective Lens Diameter
The objective lens diameter is a critical factor in determining how much light enters the binoculars, affecting image brightness. In my exploration, I found that larger objective lenses gather more light, allowing for clearer observations, especially in low-light conditions. However, it’s essential to strike a balance, as larger lenses also contribute to increased weight and bulk.
Binoculars with a moderate objective lens diameter, around 42mm, seem to offer an optimal compromise. They provide sufficient brightness while maintaining a manageable size. This balance becomes crucial for those like me who enjoy prolonged outdoor activities where the weight and portability of binoculars matter.
Eyepiece Design and Focal Length
The design of the eyepiece, coupled with the focal length, significantly influences the magnification potential of binoculars. Through my experiences, I’ve observed that longer focal lengths result in higher magnification, allowing for detailed views of distant objects. However, this comes with a trade-off, as longer focal lengths often lead to a narrower field of view.
Impact of Binocular Magnification on Image Stability: Navigating the Shifting Perspectives

Relationship between Magnification and Image Steadiness
The interplay between binocular magnification and image steadiness is a crucial consideration for any observer. In my hands-on experiences, I’ve noticed that as magnification increases, so does the sensitivity to hand movements. Even the slightest tremor becomes amplified, leading to a shaky image. This relationship is particularly noticeable at higher magnifications, where the benefits of zooming in on distant details come at the cost of image stability.
To better understand this dynamic, envision a scenario where observing wildlife or a celestial event requires magnifications beyond 10x. The challenge lies not only in locating the subject but also in maintaining a clear and steady image. This intricate dance between magnification and steadiness underscores the need for a balanced approach to binocular selection.
Challenges of Higher Magnification
While the allure of higher magnification is undeniable, it comes with its set of challenges. In my endeavors, I’ve faced the reality that binoculars with magnifications exceeding 12x present difficulties in stabilizing the image. Hand tremors, atmospheric conditions, and even the pulse in our bodies can disrupt the clarity, turning a potentially breathtaking view into a frustrating experience.
Moreover, the field of view narrows at higher magnifications, limiting the observable area. This reduction in the visible space compounds the challenge, making it harder to locate and track moving subjects. The trade-offs between magnification and stability become evident, prompting a thoughtful consideration of one’s observational needs and preferences.
Optimal Magnification for Image Stability
Finding the sweet spot for magnification becomes imperative for those seeking both detailed views and image stability. Through my trials, I’ve discovered that binoculars with magnifications up to 12x strike a harmonious balance. This range allows for enhanced zoom while mitigating the challenges associated with hand movements. It provides a stable viewing experience, making it suitable for a range of activities, from bird watching to stargazing. Choosing an optimal magnification is not just about getting closer to the subject; it’s about ensuring a steady and enjoyable observation.
Effects on Field of View and Image Brightness: Navigating the Visual Landscape
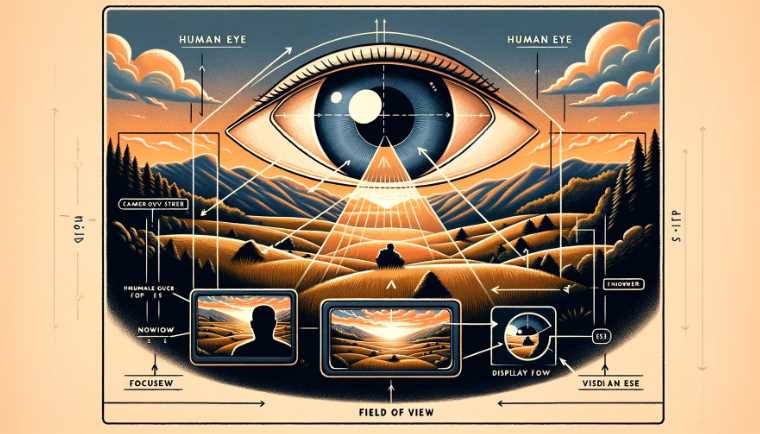
Relationship between Magnification and Field of View
The relationship between magnification and the field of view is a pivotal factor that significantly influences the observer’s experience. Through my personal exploration with binoculars, I’ve discerned that as magnification increases, the field of view tends to narrow. It’s akin to zooming in on a camera – details become more pronounced, but the overall view becomes restricted.
For instance, when observing vast landscapes or trying to locate birds in flight, a wider field of view is advantageous. Binoculars with lower magnifications, such as 8x or 10x, provide a broader perspective, allowing observers to capture more of the scene. Striking a balance between magnification and field of view becomes essential, depending on the nature of the observation.
Impact of Magnification on Image Brightness
The impact of magnification on image brightness is another critical consideration in the realm of binocular observations. From my experiences, I’ve observed that higher magnifications can result in a reduction of image brightness. This phenomenon occurs because larger magnifications often entail larger objective lenses, which, in turn, gather more light. However, this light is distributed over a more extensive area, leading to a potentially dimmer image.
Conversely, binoculars with lower magnifications and smaller objective lenses maintain better image brightness, especially in conditions with limited ambient light. This revelation becomes crucial for activities such as dawn birdwatching or stargazing, where maintaining optimal brightness enhances the overall viewing experience. Careful consideration of the intended use and lighting conditions is essential when choosing binoculars, ensuring a harmonious balance between magnification and image brightness.
Table: Comparison of Magnification Levels and Their Effects
| Magnification | Field of View | Image Brightness | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8x | Wider | Bright | General Observation |
| 10x | Moderate | Balanced | Bird Watching, Sports |
| 12x | Narrow | Diminished | Detailed Observations |
This table offers a quick reference guide, summarizing the impact of different magnification levels on the field of view, image brightness, and recommended use.
Choosing the Right Magnification for Different Applications
General Recommendations for Binocular Magnification
When it comes to binocular magnification, adhering to general recommendations serves as a solid foundation for choosing the right instrument. In my own pursuits, I’ve discovered that magnifications ranging from 8x to 12x are commonly endorsed for various activities. This range strikes a balance between detailed observations and image stability, making it suitable for general use.
Specific Applications and Magnification Guidelines
Diverse activities demand tailored magnification guidelines to ensure optimal viewing experiences. Bird watching, for instance, benefits from moderate magnifications around 8x to 10x, providing a wider field of view for tracking avian movements. Astronomy enthusiasts, on the other hand, often lean towards higher magnifications, such as 12x, for detailed celestial observations.
In my personal encounters with different applications, I’ve found that understanding the specific requirements of each activity is crucial. Tailoring the magnification to the task at hand enhances the observer’s ability to extract meaningful details and fully immerse themselves in the experience.
Table: Recommended Binocular Magnifications for Various Applications
| Activity | Recommended Magnification | Observational Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Bird Watching | 8x – 10x | Wider field of view for tracking movement |
| Stargazing | 12x | Detailed celestial observations |
| Sports Events | 10x | Balanced magnification for dynamic scenes |
| Nature Observation | 8x – 12x | Versatile range for various scenarios |
This table offers a quick reference guide, suggesting magnifications tailored to specific activities. It helps enthusiasts make informed choices, aligning their binocular magnification with the unique demands of each observational pursuit.
Importance of Balancing Zoom and Image Stability
In the quest for the perfect binocular magnification, finding a harmonious balance between zoom and image stability is paramount. Too much magnification may compromise steadiness, while too little may sacrifice detailed observations. Striking this delicate equilibrium ensures an enjoyable and effective viewing experience across a spectrum of activities.
Comparison of Binocular Magnifications: Navigating the Options
Magnification Levels
The choice of binocular magnification significantly influences the viewing experience. Common magnification levels include 8x, 10x, and 12x, each offering a distinct perspective on the observed subject.
Image Stability Rating
Image stability is a critical aspect of binocular performance. Lower magnifications, like 8x, generally provide steadier images, while higher magnifications, such as 12x, may present challenges in maintaining stability, especially without additional stabilization features.
Field of View
The field of view is influenced by magnification, affecting how much of the scene is visible. Lower magnifications, like 8x, offer a wider field, beneficial for activities like bird watching. Higher magnifications, like 12x, narrow the field but provide more detailed views.
Brightness
Brightness is influenced by both magnification and objective lens diameter. While higher magnifications may reduce brightness, factors like lens coatings can mitigate this. Balancing magnification and brightness is crucial for optimal viewing in various lighting conditions.
Recommended Applications
Different magnifications cater to specific activities. For general use, 8x to 10x magnifications are versatile, while 12x may be preferred for detailed observations like stargazing. Matching magnification to the intended application enhances the viewing experience.
Table: Comparison of Binocular Magnifications
| Magnification | Image Stability | Field of View | Brightness | Recommended Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8x | High | Wider | Balanced | General Observations, Bird Watching |
| 10x | Moderate | Moderate | Balanced | Sports Events, Nature Observation |
| 12x | Challenging | Narrow | Potential Diminished | Detailed Observations, Stargazing |
This table provides a succinct overview, allowing enthusiasts to compare binocular magnifications based on image stability, field of view, brightness, and recommended applications.
Final Words
In the world of binocular observations, the choice of magnification is a nuanced decision, blending personal preferences with practical considerations. Through my own experiences, I’ve come to appreciate the delicate balance between zoom and stability, recognizing each magnification level’s unique advantages.
Whether scanning the skies or exploring the intricate details of nature, the right magnification transforms mere observation into an immersive journey. As you embark on your own ventures, consider the insights shared here and let your chosen magnification be the key to unlocking the wonders that await through the lenses of your binoculars. Happy exploring!
Resources and References
- OpticsPlanet – Binoculars Buying Guide
- Cornell Lab of Ornithology – Choosing Binoculars for Bird Watching
- Sky & Telescope – A Guide to Binoculars for Astronomy

I am an enthusiastic student of optics, so I may be biased when I say that optics is one of the most critical fields. It doesn’t matter what type of optics you are talking about – optics for astronomy, medicine, engineering, or pleasure – all types are essential.