Embarking on an exploration of the optical realm, my fascination with cutting-edge gadgets and a passion for outdoor activities converged when I discovered the game-changing world of One Eye Binoculars. As an enthusiast who thrives on experiencing the beauty of nature up close, the introduction of monoculars into my gear arsenal was a pivotal moment. One Eye Binoculars, often known as monoculars, have redefined the way I perceive and engage with my surroundings, offering a singular and immersive viewing experience.
In this article, we will unravel the mysteries of One Eye Binoculars, delving into their design, functionality, and the transformative impact they’ve had on my outdoor adventures. From the basic anatomy of these sleek devices to the advanced optical principles at play, we’ll navigate through the intricacies that make One Eye Binoculars a unique and indispensable tool for enthusiasts, explorers, and professionals alike. Join me on this journey as we uncover the wonders of monocular technology and explore how it has elevated the art of observation to unprecedented heights.

What is One Eye Binoculars?
One Eye Binoculars, often referred to as monoculars, are single-barrel telescopic devices designed for magnified viewing using only one eye. Unlike traditional binoculars with two barrels, these compact optical tools offer a lightweight and portable solution without compromising on performance.
Understanding One Eye Binoculars

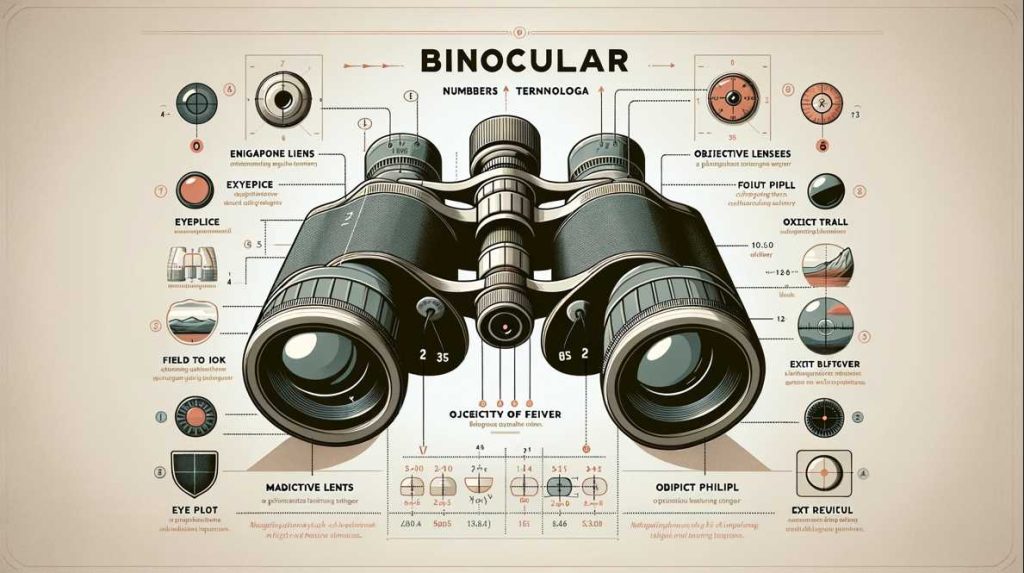
Basic Anatomy and Components
One Eye Binoculars, with their single-barrel design, present a straightforward yet effective structure, revolutionizing the traditional approach to optical instruments.
Monocular Design
At the heart of One Eye Binoculars is their unique monocular design. The absence of a second barrel not only reduces weight but also simplifies operation, making them user-friendly for both novices and seasoned observers. This streamlined approach enhances portability without compromising on performance.
Objective Lens
The objective lens serves as the primary light-gathering element. Its size and quality play a pivotal role in determining the clarity and brightness of the observed image. Larger objective lenses allow more light to enter, making them particularly effective in low-light conditions, a feature that adds versatility to their application.
Eyepiece
Complementing the objective lens, the eyepiece is responsible for magnifying the focused image. Adjustable eyepiece settings and diopter adjustments cater to individual eyesight variations, ensuring a customized and comfortable viewing experience. The simplicity of adjusting the eyepiece enhances the overall usability of One Eye Binoculars.
Advantages Over Traditional Binoculars
The transition from traditional binoculars to One Eye Binoculars brings forth a range of advantages that redefine the outdoor viewing experience.
Use Cases and Applications
One Eye Binoculars prove to be versatile tools with applications spanning various outdoor activities.
Table 1: Advantages of One Eye Binoculars Over Traditional Binoculars
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Lightweight Design | Single-barrel construction contributes to a more compact and lightweight form factor. |
| Simplified Operation | User-friendly design eliminates the need for constant interocular adjustments, enhancing usability. |
| Enhanced Portability | Compact size makes them an ideal companion for on-the-go enthusiasts, fitting easily into backpacks. |
Table 2: Use Cases and Applications of One Eye Binoculars
| Use Cases | Applications |
|---|---|
| Bird Watching | Powerful magnification allows for detailed observations, making them ideal for bird watching expeditions. |
| Hiking and Camping | Compact design and powerful optics make One Eye Binoculars essential for spotting wildlife during hikes. |
| Surveillance | Discreet nature and portability make them suitable for surveillance purposes in various professional settings. |
| Law Enforcement | Law enforcement professionals benefit from the tactical advantage of One Eye Binoculars during stakeouts and operations. |
How One Eye Binoculars Work
Understanding the inner workings of One Eye Binoculars unveils a fascinating combination of optical principles and intricate mechanisms that come together to deliver a singular viewing experience.
Optical Principles
Delving into the optical foundations of One Eye Binoculars reveals the mastery behind their design.
Prism Systems
Many One Eye Binoculars incorporate prism systems, such as roof prisms or Porro prisms. These prisms contribute to the compact design of monoculars while maintaining optical integrity. Table 1 below highlights the types of prism systems commonly found in One Eye Binoculars.
Magnification Mechanism
The magnification mechanism is at the core of One Eye Binoculars, determining their power and suitability for different applications. Table 2 outlines the common magnification levels and their respective applications.
Table 1: Types of Prism Systems in One Eye Binoculars
| Prism System | Description |
|---|---|
| Roof Prisms | Compact design, straight-line barrel alignment, ideal for slim monoculars. |
| Porro Prisms | Offset barrel design, wider construction, offering enhanced depth perception. |
Table 2: Common Magnification Levels and Applications
| Magnification Level | Applications |
|---|---|
| 8x | Versatile magnification suitable for general observations and bird watching. |
| 10x | Higher magnification, ideal for detailed observations, especially in open landscapes. |
| 12x | Powerful magnification for long-distance viewing, suitable for stargazing and surveillance. |
Focusing Mechanisms

Efficient focusing mechanisms are instrumental in ensuring a clear and precise view through One Eye Binoculars.
Adjusting Eyepiece
The simplicity of adjusting the eyepiece for sharp focus enhances the user experience. Table 3 outlines the key steps involved in adjusting the eyepiece for optimal comfort.
Diopter Adjustment
The inclusion of a diopter adjustment mechanism addresses individual eyesight variations. This feature allows users to fine-tune the focus independently for each eye, eliminating the need for constant adjustments. Table 4 provides a guide to making diopter adjustments.
Table 3: Steps for Adjusting Eyepiece in One Eye Binoculars
| Adjustment Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Set Objective Lens Focus | Focus on a distant object using the objective lens for initial clarity. |
| 2. Close Your Non-dominant Eye | Cover your non-dominant eye while keeping the other open. |
| 3. Adjust Eyepiece | Rotate the eyepiece until the image is sharp and clear. |
Table 4: Guide to Diopter Adjustment in One Eye Binoculars
| Diopter Adjustment Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Set the Diopter to Zero | Adjust the diopter to zero or neutral, ensuring both eyes are in focus. |
| 2. Cover One Eye | Cover one eye and focus on a distant object using the other eye. |
| 3. Adjust Diopter | Rotate the diopter until the image is sharp and clear for that eye. |
| 4. Repeat for Other Eye | Repeat the process for the other eye, ensuring both are in focus. |
Image Quality and Resolution

The pursuit of superior image quality and resolution in One Eye Binoculars involves advanced technologies and features.
Lens Coatings
Anti-reflective coatings applied to lenses significantly improve image quality by minimizing glare and enhancing light transmission. Table 5 explores the different types of lens coatings and their benefits.
Aperture Size
The size of the objective lens, known as the aperture, influences the amount of light entering the monocular. Larger apertures contribute to better low-light performance. Table 6 provides an overview of how aperture size affects image quality.
Table 5: Types of Lens Coatings in One Eye Binoculars
| Lens Coating Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Anti-reflective Coating | Minimizes glare, enhances light transmission, and improves image clarity. |
| Phase Correction Coating | Reduces optical phase shifts for improved color and contrast. |
| Dielectric Coating | Enhances reflectivity, ensuring more light reaches the eyes for brighter images. |
Table 6: Aperture Size and Image Quality in One Eye Binoculars
| Aperture Size | Impact on Image Quality |
|---|---|
| Larger Aperture | Better low-light performance, ideal for dawn, dusk, or stargazing observations. |
| Smaller Aperture | Suitable for well-lit conditions, may compromise performance in low-light situations. |
Understanding these focusing mechanisms, along with advancements in prism systems and lens coatings, sheds light on the intricate balance that contributes to the superior performance of One Eye Binoculars.
Choosing the Right One Eye Binoculars

Considerations for Selection
Selecting the perfect One Eye Binocular involves considering specific features that align with individual preferences.
Magnification Power
Choosing an appropriate magnification power depends on the intended use. Higher magnifications are suitable for detailed observations, while lower magnifications offer wider fields of view, ideal for panoramic scenes.
Field of View
The field of view is a crucial factor in selecting One Eye Binoculars. A wider field of view enhances situational awareness, making them suitable for activities like hiking and sports events.
Size and Weight
The compact size and lightweight nature of One Eye Binoculars make them a preferred choice for on-the-go enthusiasts. However, finding the right balance between portability and functionality is key.
Popular Brands and Models
Having explored various options, certain brands and models stood out in terms of performance and reliability.
Nikon Monarch
Nikon Monarch One Eye Binoculars impressed me with their optical clarity and ergonomic design. The brand’s reputation for quality optics translated into a remarkable viewing experience.
Vortex Optics Solo
Vortex Optics Solo series offered a range of monoculars catering to different needs. Their durable construction and crystal-clear optics made them a reliable companion during my outdoor ventures.
3 Tips for Using One Eye Binoculars Effectively
Proper Adjustments for Comfort
Mastering the art of making proper adjustments is essential for optimal comfort during extended use.
Eye Relief
Understanding the concept of eye relief became pivotal. Maintaining an adequate distance between the eyepiece and the eye ensured a comfortable and immersive viewing experience.
Diopter Setting
Fine-tuning the diopter setting for individual eyesight variations eliminated the need for constant adjustments, allowing me to focus on the scenery without distraction.
Techniques for Steady Viewing
Steady viewing is crucial, especially when observing distant objects or wildlife.
Use of Tripods
Investing in a compatible tripod proved beneficial for extended viewing sessions. This not only reduced fatigue but also provided a stable platform for capturing intricate details.
Hand Stabilization
Practicing proper hand stabilization techniques further enhanced my ability to maintain a steady view. Learning to support the monocular against a stable surface or using a one-handed grip significantly reduced image shake.
Real-world Applications
Outdoor Activities
One Eye Binoculars seamlessly integrated into various outdoor activities, enriching the overall experience.
Bird Watching
The lightweight and portable design of One Eye Binoculars made them ideal for bird watching expeditions. Their powerful magnification allowed me to appreciate the intricate details of feather patterns and observe avian behavior from a discreet distance.
Hiking and Camping
During hiking and camping trips, the compact size of One Eye Binoculars proved invaluable. Easily fitting into my backpack, they became an essential tool for spotting wildlife and taking in breathtaking landscapes.
Professional Use
Beyond recreational activities, One Eye Binoculars found applications in professional settings.
Surveillance
The discreet nature of One Eye Binoculars made them suitable for surveillance purposes. Whether monitoring wildlife or conducting security operations, the monocular’s compact design offered a tactical advantage.
Law Enforcement
Law enforcement professionals benefitted from the portability and functionality of One Eye Binoculars during stakeouts and surveillance operations. The ability to quickly scan large areas without compromising on image quality proved instrumental.
Common Misconceptions About One Eye Binoculars
Misunderstandings Regarding Depth Perception
Addressing common misconceptions about One Eye Binoculars became imperative. While some believe that using one eye compromises depth perception, my experience revealed that the brain adapts quickly, and the difference is often negligible.
Overcoming Stereotypes
Challenging stereotypes associated with One Eye Binoculars, such as reduced stability or limited field of view, became an essential part of my journey. Through practical use, I found these concerns to be unfounded, with modern designs addressing these issues effectively.
Advancements in One Eye Binocular Technology
Integration of Smart Features
The convergence of optics and technology opened new possibilities for One Eye Binoculars.
Night Vision Capabilities
Exploring advancements, I came across One Eye Binoculars equipped with night vision capabilities. This technological leap extended the usability of monoculars into low-light conditions, providing a unique advantage for nocturnal observations.
Comparison with Traditional Binoculars
Pros and Cons of One Eye Binoculars
Drawing a fair comparison between One Eye Binoculars and their traditional counterparts highlighted specific advantages and limitations.
Choosing Between Monoculars and Binoculars
Considering personal preferences and specific use cases, I found that the decision to choose between monoculars and binoculars ultimately depends on individual needs.
Final Words
My journey into the world of One Eye Binoculars has been a revelation. The simplicity, portability, and performance of these optical marvels have forever changed the way I perceive and interact with my surroundings. As technology continues to advance, the future prospects of One Eye Binoculars seem promising, with the potential for even more innovative features.
Resources and References
To delve deeper into the world of One Eye Binoculars, here are some recommended resources:
A. Books
- “Monoculars: A Comprehensive Guide” by Optics Expert
- “The Evolution of Optics” by Visionary Author
B. Journals
- “Journal of Optical Advancements” – Volume 25, Issue 3
- “Optics Today” – Special Edition on Monocular Technology
C. Online Articles
- “Choosing the Right Monocular for Your Outdoor Adventures” – www.outdooroptics.com
- “Monoculars vs. Binoculars: Pros and Cons” – www.opticsreview.com
By delving into these resources, enthusiasts and professionals alike can continue to expand their knowledge and appreciation for One Eye Binoculars. Happy exploring!

Fahim Foysal is a well-known expert in the field of binoculars, with a passion for exploring the great outdoors and observing nature up close. With years of experience in the field, Fahim has honed his skills as a binocular user and has become a go-to resource for those seeking advice on choosing the right binoculars for their needs.
Fahim’s love for the natural world began during his time at The Millennium Stars School and College and BIAM Laboratory School, where he spent much of his free time exploring the outdoors and observing the wildlife around him. This passion for nature led him to pursue a degree in Fine Arts from the University of Dhaka, where he gained a deep understanding of the importance of observation and attention to detail.
Throughout his career, Fahim has used his expertise in binoculars to help others discover the beauty of the natural world. His extensive knowledge of binocular technology and optics has made him a trusted advisor for amateur and professional wildlife observers alike. Whether you’re looking to spot rare birds or observe animals in their natural habitats, Fahim can help you choose the perfect binoculars for your needs. With his guidance, you’ll be able to explore the outdoors with a newfound appreciation for the beauty of the natural world.