Toenail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common fungal infection that affects the toenails. The responsible fungi, usually dermatophytes or yeast, can invade the nail bed and cause various changes to the nail’s appearance. When examined under a microscope, the following characteristics may be observed:
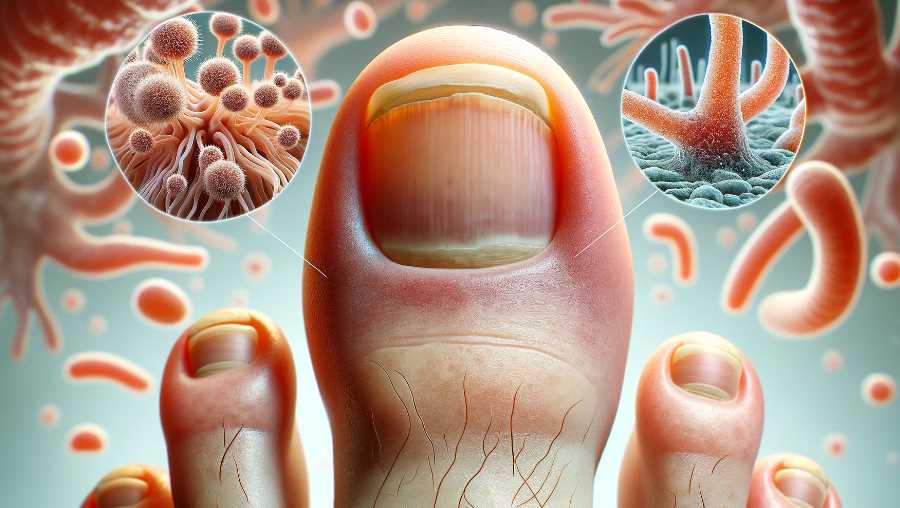
- Hyphae: Fungal hyphae are the thread-like structures that make up the body of the fungus. These hyphae may be visible under a microscope and can penetrate the affected toenail tissues.
- Spores: Fungal spores, also known as conidia, are reproductive structures that allow the fungus to spread and reproduce. They may be present in various forms, such as chains or clusters, and their size and shape can provide clues about the specific type of fungus causing the infection.
- Color and Texture: The color and texture of the toenail tissue can be observed. In cases of toenail fungus, the affected nail may appear discolored, usually yellow or brown, and may become thickened or brittle. The presence of fungal elements contributes to these changes.
- Invasion of Nail Tissues: The microscopic examination may reveal the extent of the fungus’s invasion into the nail tissues. Fungi can invade the nail plate, nail bed, and surrounding structures, leading to visible damage.
- Identification of Fungal Species: In some cases, a laboratory may culture the fungus from a nail sample to identify the specific species responsible for the infection. This can help in determining the most effective treatment.
Here’s a simple table summarizing some features:
| Feature | Microscopic Observation |
|---|---|
| Hyphae | Branched, thread-like structures penetrating the nail tissue. |
| Sporulation | Presence of spores or conidia, which are reproductive structures. |
| Color and Texture Changes | Discoloration (yellow or brown) and changes in texture (thickening, brittleness). |
| Invasion of Nail Tissue | Fungus may invade the nail plate, nail bed, and surrounding tissues, causing visible damage. |
Keep in mind that a definitive diagnosis often requires laboratory testing, such as a fungal culture or polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis.
Anatomy of Toenail Fungus

Overview of Fungal Infection
Toenail fungus, scientifically known as onychomycosis, is a common ailment affecting millions worldwide. This fungal infection is primarily caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive in warm and moist environments. Candida and molds can also contribute to toenail fungal infections. As someone who has grappled with this condition, I understand the urgency of unraveling its complexities.
Types of Fungi Causing Toenail Infections
| Type of Fungi | Common Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Dermatophytes | Thrive in warm, moist environments |
| Candida | Opportunistic fungus, can affect nails |
| Molds | Variety of species contributing to infections |
Factors Contributing to Toenail Fungus
Several factors create a conducive environment for toenail fungus to take root and thrive. Personal hygiene, exposure to damp conditions, and compromised immune systems are key contributors. Reflecting on my own experience, it’s evident that understanding these factors is crucial for effective prevention and management.
Factors Contributing to Toenail Fungus
| Contributing Factor | Impact on Toenail Fungus |
|---|---|
| Poor Hygiene Practices | Fungal growth due to unclean conditions |
| Damp Environments | Fungi thrive in moist, warm areas |
| Weakened Immune System | Reduced ability to combat fungal infections |
Physical Characteristics of Infected Toenails
Identifying toenail fungus goes beyond recognizing visible symptoms. Under the microscope, the physical characteristics of infected toenails reveal intricate details about the severity and type of infection. Personally observing these characteristics has provided valuable insights into the nature of the condition.
Physical Characteristics of Infected Toenails
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Discoloration | Yellowing, brown spots, or white streaks |
| Thickening | Increased nail thickness, brittleness |
| Distorted Shape | Altered nail shape and structure |
| Debris Accumulation | Buildup of debris under the nail |
| Separation from Nail Bed | Lifting of the nail from the nail bed |
Understanding the intricacies of toenail fungus at a microscopic level equips individuals with the knowledge to address the infection comprehensively. This insight extends beyond recognizing symptoms to understanding the very nature of the fungi causing the condition and the environmental factors that contribute to its persistence.
Microscopic Examination
Techniques for Microscopic Analysis
Microscopic examination is the key to unraveling the hidden world of toenail fungus. Two primary techniques — light microscopy and electron microscopy — play a pivotal role in visualizing the intricate details of fungal structures. Having undergone these examinations myself, I can attest to the transformative power of these techniques in understanding the microscopic landscape of toenail infections.
Techniques for Microscopic Analysis
| Microscopic Technique | Resolution | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Light Microscopy | Lower magnification | Examining overall nail and fungal structures |
| Electron Microscopy | Higher magnification | Detailed examination of fungal elements |
1. Light Microscopy
Light microscopy provides a broad overview of toenail fungus, allowing for the observation of general structures and the interaction between fungi and nail tissues. While it may lack the resolution of electron microscopy, it remains a valuable tool in initial assessments.
2. Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy, with its higher magnification capabilities, takes us deeper into the microscopic world. It enables the visualization of fine details, including individual fungal cells, providing insights that are invaluable for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Visualizing Fungal Structures
Understanding toenail fungus requires a close examination of its building blocks. The visualizing of fungal structures under the microscope unveils a hidden landscape teeming with life. This section explores the two fundamental aspects of fungal structures: hyphae and mycelium, and spores and conidia.
Fungal Structures Under Microscopic Analysis
| Fungal Structure | Description |
|---|---|
| Hyphae and Mycelium | Thread-like structures and their collective mass |
| Spores and Conidia | Reproductive structures responsible for fungal spread |
1. Hyphae and Mycelium
Hyphae are the essential building blocks of toenail fungus, forming intricate networks known as mycelium. Light microscopy allows for the observation of these structures, offering insights into the extent and density of the fungal invasion within the nail.
2. Spores and Conidia
Spores and conidia represent the reproductive elements of toenail fungus. These microscopic entities play a crucial role in the spread of the infection. Electron microscopy, with its high resolution, enables a detailed examination of these structures, aiding in the identification of specific fungal species.
Insights from Microscopic Observations
Identifying Fungal Species
Microscopic observations offer a gateway to precise identification of fungal species responsible for toenail infections. Having personally experienced the anticipation that comes with awaiting these results, I can attest to the significance of this aspect of microscopic analysis. Light microscopy provides a preliminary view, while electron microscopy delves into finer details, aiding in the differentiation of various fungal species.
Common Fungal Species Identified Through Microscopy
| Fungal Species | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Trichophyton | Fine hyphae, often causing white or yellow discoloration |
| Candida | Ovoid yeast cells, associated with a whitish appearance |
| Aspergillus | Septate hyphae, linked to green or black discoloration |
Understanding the Severity of Infection
Microscopic findings not only identify the culprit but also unveil the extent of toenail fungus infection. Examining the density and distribution of hyphae and mycelium provides critical insights into the severity of the condition. This firsthand understanding has reinforced the importance of early detection and intervention.
Microscopic Indicators of Infection Severity
| Severity Level | Microscopic Indicators |
|---|---|
| Mild | Sparse hyphae, limited mycelium presence |
| Moderate | Increased hyphae density, expanding mycelium network |
| Severe | Dense hyphal invasion, extensive mycelium throughout the nail |
Link between Microscopic Findings and Symptoms
Microscopic observations form a bridge between the hidden world of fungi and the visible symptoms experienced by individuals. Understanding this link is crucial for tailoring effective treatment plans. For instance, the presence of spores and conidia might indicate a higher risk of spreading the infection. Recognizing this connection empowers both patients and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about the most appropriate course of action.
Connecting Microscopic Findings with Visible Symptoms
| Microscopic Findings | Corresponding Visible Symptoms |
|---|---|
| High Hyphal Density | Thickening, discoloration, and distortion of the nail |
| Presence of Spores and Conidia | Increased risk of spreading to adjacent nails or skin |
| Reduced Hyphal Density | Potential signs of treatment effectiveness |
In summary, microscopic observations provide a comprehensive understanding of toenail fungus, from identifying the specific fungal species to assessing the severity of infection and establishing a direct link with visible symptoms. This knowledge forms the cornerstone for effective diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies.
Factors Affecting Toenail Fungus Growth
Toenail fungus is a resilient intruder, and understanding the factors that fuel its growth is paramount for effective prevention and management. Drawing from personal experiences, I’ve come to recognize three key influencers—environmental conditions, host factors, and lifestyle choices—that significantly impact toenail fungus development.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which our feet reside plays a crucial role in toenail fungus growth. Dark, damp, and warm conditions create an ideal breeding ground for fungi. Public places like swimming pools, gyms, and communal showers often harbor these conditions, contributing to the increased risk of infection. Acknowledging the role of environmental factors empowers individuals to be vigilant in spaces where the risk of exposure is heightened.
Environmental Conditions and Toenail Fungus Growth
| Environmental Factor | Influence on Toenail Fungus Growth |
|---|---|
| Humidity | Fungi thrive in moist environments |
| Poor Ventilation | Limited airflow promotes fungal growth |
| Shared Spaces | Increased risk of exposure in communal areas |
Host Factors
Individual susceptibility to toenail fungus varies, with certain host factors influencing the likelihood of infection. Weakened immune systems, pre-existing health conditions, and genetic predispositions can contribute to an increased vulnerability to fungal invasions. As I navigated my own battle with toenail fungus, understanding these host factors became crucial in crafting a holistic approach to treatment and prevention.
Host Factors and Toenail Fungus Susceptibility
| Host Factor | Impact on Toenail Fungus Susceptibility |
|---|---|
| Weakened Immune System | Reduced ability to fend off fungal infections |
| Pre-existing Conditions | Certain health issues increase susceptibility |
| Genetics | Familial predisposition may elevate risk |
Impact of Lifestyle Choices
Our daily habits and choices also significantly influence toenail fungus growth. Personal hygiene practices, footwear choices, and exposure to potential sources of infection all contribute to the equation. Reflecting on my own journey, modifying certain lifestyle choices played a pivotal role in preventing recurrence and fostering overall nail health.
Lifestyle Choices and Toenail Fungus Impact
| Lifestyle Choice | Influence on Toenail Fungus Growth |
|---|---|
| Hygiene Practices | Regular cleaning reduces the risk of infection |
| Footwear Selection | Breathable, dry footwear discourages fungal growth |
| Exposure to Risky Environments | Awareness and precautions in communal spaces |
Treatment Approaches Based on Microscopic Analysis
Microscopic analysis not only aids in the diagnosis of toenail fungus but also serves as a compass guiding treatment decisions. In my journey, the insights gained through this analysis have played a pivotal role in navigating the diverse landscape of treatment options.Antifungal Medications
1. Topical Treatments
Microscopic analysis helps determine the extent of surface-level fungal invasion, guiding the choice of topical treatments. Antifungal nail creams, ointments, and lacquers become viable options for infections that are limited to the nail’s surface. Through personal experience, I found that consistent application, coupled with regular nail trimming, is essential for effective topical treatment.
2. Oral Medications
For more severe cases, where microscopic observations reveal deep-rooted fungal networks, oral medications come into play. These systemic antifungal drugs circulate through the bloodstream, reaching the nail bed and effectively targeting the infection at its source. However, the decision to opt for oral medications should be carefully considered, taking into account potential side effects and individual health factors.
Antifungal Medications and Microscopic Guidance
| Treatment Type | Microscopic Guidance |
|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | Limited fungal invasion on the nail surface |
| Oral Medications | Deep-rooted fungal networks requiring systemic treatment |
Surgical Interventions
1. Nail Removal
In cases where toenail fungus has caused irreparable damage and microscopic analysis reveals extensive invasion, surgical interventions may be necessary. Nail removal, either partial or complete, becomes a viable option. This procedure allows for the direct treatment of the underlying infection, facilitating the application of antifungal medications to the nail bed.
2. Laser Therapy
Laser therapy, guided by microscopic insights, has emerged as a promising non-invasive option. Laser light targets the fungal cells, disrupting their structure and inhibiting growth. Microscopic analysis aids in determining the effectiveness of laser therapy, providing a targeted approach for cases where traditional treatments may fall short.
Surgical Interventions and Microscopic Guidance
| Intervention | Microscopic Guidance |
|---|---|
| Nail Removal | Extensive fungal invasion requiring direct treatment |
| Laser Therapy | Targeted approach for cases where traditional treatments may fall short |
Prevention Strategies Informed by Microscopic Understanding
Armed with insights from microscopic analysis, effective prevention strategies can be tailored to create an inhospitable environment for toenail fungus. As someone who has witnessed the microscopic intricacies of this condition, I understand the significance of proactive measures in maintaining optimal foot health.
Personal Hygiene Practices
Microscopic analysis reveals the vulnerability of nails to fungal invasions under certain conditions. Prioritizing meticulous personal hygiene practices becomes a fundamental aspect of prevention. Regularly cleaning and drying the feet, especially in between the toes, minimizes the risk of fungal growth. Trimming nails with clean tools and avoiding sharing personal grooming items are additional steps informed by microscopic understanding.
Footwear and Sock Choices
Microscopic examination sheds light on how fungi thrive in dark, damp environments. Choosing breathable footwear that allows proper ventilation can significantly reduce the risk of toenail fungus. Opting for moisture-wicking socks, preferably made from natural fabrics, aids in keeping feet dry. These preventive measures, grounded in microscopic insights, contribute to creating an environment where fungi struggle to flourish.
Regular Check-ups and Early Intervention
Microscopic analysis not only aids in diagnosis but emphasizes the importance of regular check-ups. Periodic visits to healthcare professionals, especially for those with a history of toenail fungus, can facilitate early detection of potential issues. This proactive approach enables swift intervention, preventing the escalation of fungal infections. Early identification of microscopic indicators prompts timely treatment, reducing the impact on nail health.
Role of Research in Advancing Microscopic Diagnosis
Microscopic diagnosis of toenail fungus has witnessed significant advancements through ongoing research endeavors. These developments not only deepen our understanding of the condition but also pave the way for more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment options.
Recent Studies on Toenail Fungus
Recent studies delve into the molecular and genetic aspects of toenail fungus, unraveling new insights into the diverse species responsible for infections. These findings inform the refinement of diagnostic criteria, aiding in the identification of specific fungal strains through microscopic analysis.
Technological Innovations in Microscopy
Cutting-edge technological innovations in microscopy, such as high-resolution imaging and advanced staining techniques, have revolutionized the field. These innovations enable a more detailed and precise examination of fungal structures, enhancing the diagnostic capabilities of microscopic analysis.
Future Prospects for Improved Diagnosis and Treatment
The ongoing trajectory of research holds promise for improved toenail fungus diagnosis and treatment. Future prospects include the development of rapid diagnostic tools, targeted therapies based on individual fungal profiles, and advancements in preventive measures. The collaborative efforts of researchers, clinicians, and technologists contribute to a future where microscopic diagnosis becomes even more precise and impactful in the management of toenail fungus.
Final Words
Embarking on the microscopic journey into toenail fungus has unraveled a hidden world beneath the surface. From identifying fungal species to understanding the severity of infection and linking microscopic findings to visible symptoms, this exploration provides a holistic perspective. Microscopic analysis not only guides treatment decisions but also informs preventive strategies. As research continues to advance the field, promising future prospects for improved diagnosis and treatment beckon. Armed with these insights and resources, individuals can navigate their path to healthier toenails, fostering a proactive approach to foot health and overall well-being.
Resources and References
For those seeking a deeper understanding of toenail fungus and microscopic diagnosis, the following resources and references provide valuable insights:
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Journal of Medical Mycology

Fahim Foysal is a well-known expert in the field of binoculars, with a passion for exploring the great outdoors and observing nature up close. With years of experience in the field, Fahim has honed his skills as a binocular user and has become a go-to resource for those seeking advice on choosing the right binoculars for their needs.
Fahim’s love for the natural world began during his time at The Millennium Stars School and College and BIAM Laboratory School, where he spent much of his free time exploring the outdoors and observing the wildlife around him. This passion for nature led him to pursue a degree in Fine Arts from the University of Dhaka, where he gained a deep understanding of the importance of observation and attention to detail.
Throughout his career, Fahim has used his expertise in binoculars to help others discover the beauty of the natural world. His extensive knowledge of binocular technology and optics has made him a trusted advisor for amateur and professional wildlife observers alike. Whether you’re looking to spot rare birds or observe animals in their natural habitats, Fahim can help you choose the perfect binoculars for your needs. With his guidance, you’ll be able to explore the outdoors with a newfound appreciation for the beauty of the natural world.
Table of Contents